It’s estimated that more than 37 million Americans have diabetes, and are responsible for managing high blood pressure and the other symptoms that come with the condition.
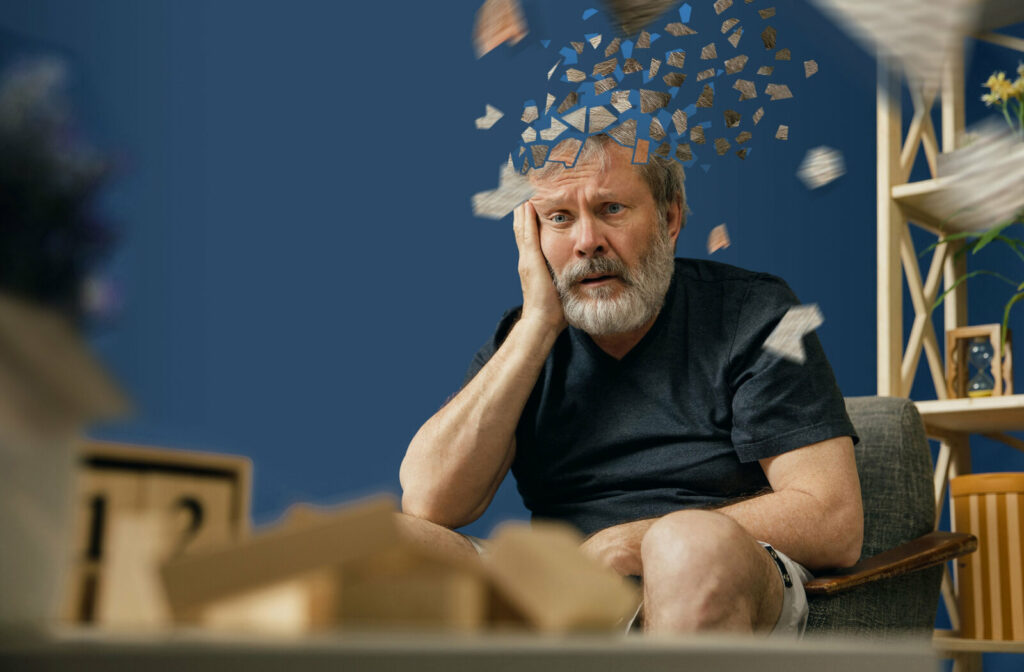
If not properly managed, diabetes can lead to more severe complications and harm your overall health, including cognitive issues like memory loss. If the challenges of managing diabetes or memory loss are becoming too complicated, it may be valuable to consider assisted living.
Our experienced and friendly staff at Meadowcrest at Middletown are happy to discuss further the benefits of joining our family-oriented community.
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Memory?
Diabetes that is poorly managed can lead to more severe complications that can affect your cognitive abilities. This can sometimes include memory loss or even the risk of progressive dementia.
A typical symptom of diabetes is high blood glucose levels, which are capable of causing damage to nerve cells, glial cells, and blood cells in the body or brain. Damaging these nerves can affect the command centre of your brain and result in memory loss, among other cognitive issues. Therefore, poorly managed diabetes is more likely to result in dementia.
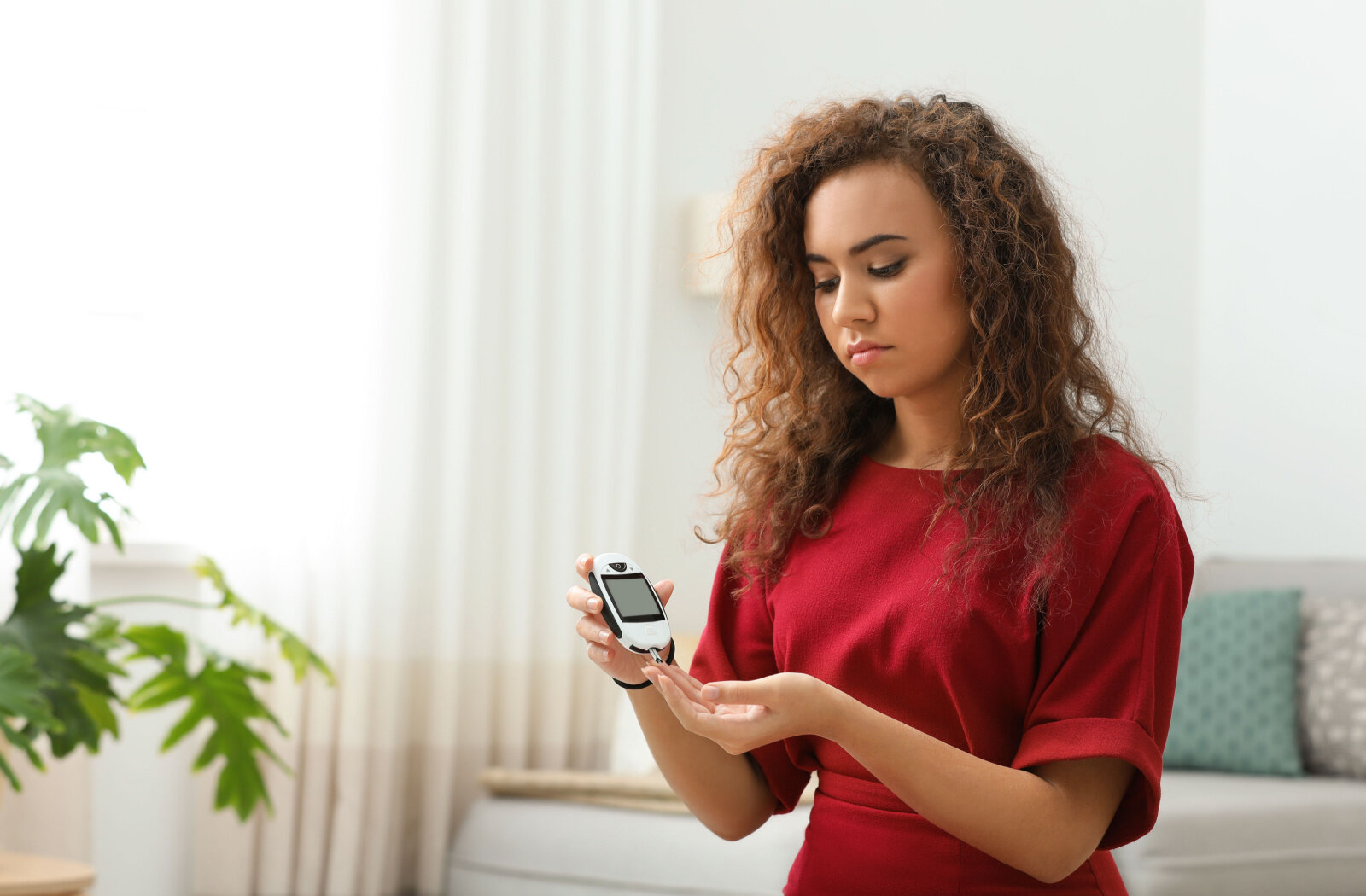

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is an incurable health condition that impacts how your body converts food into energy. It affects the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin which is needed by the body to manage blood sugar levels.
Insulin
The body needs insulin to properly manage blood sugar levels by facilitating it in entering the body’s cells for use and then storing the residual within the liver for use later on. Without insulin, your blood sugar is not adequately regulated, and too much glucose in your blood can lead to numerous health problems.
Different Types of Diabetes
Diabetes can be present in different stages and forms, with varying implications. The chronic condition is believed to affect about 1 in 10 Americans, with 90-95% having the most common form of type 2.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is commonly identified early in children, teens, and younger adults. It is an autoimmune issue in which the body is essentially attacking itself. Some of the symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Bed-wetting or the need to urinate more frequently than normal
- Irritability or mood changes
- Weight loss
- Blurry vision or feeling dizzy
- Thirst and hunger
- Fatigue or feeling weak
Type 2 Diabetes
In contrast to type 1, type 2 diabetes is typically diagnosed in adults and develops slowly over time. Symptoms are not always apparent with type 2 diabetes, and it is vital to regularly check your blood sugar if you believe you may be at risk.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops in women during pregnancy and typically resolves itself after the baby’s birth. Nonetheless, it can put you at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later on or pose health issues for the baby.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is when someone has higher than normal blood sugar levels but has not yet reached the point of type 2 diabetes. Like type 2 diabetes, symptoms are not always apparent, and monitoring your blood sugar levels is crucial. Here are a few of the potential factors that might indicate prediabetes:
- You’re overweight
- You’re above the age of 45
- You have immediate family with type 2 diabetes
- You’ve had gestational diabetes
- You are not physically active
How to Test for Diabetes?
Diabetes can develop in anyone, and it is crucial to get tested if you exhibit any signs or symptoms. Testing for diabetes will almost always take place through a blood test and laboratory results. Here are some of the standard tests your doctor may recommend:
- A1C Test
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test
- Glucose Tolerance Test
- Random Blood Sugar Test
For more information, reach out to your doctor and discuss your options for testing and treating diabetes.
Diabetes Management
Unfortunately, there is no cure for diabetes, but with proper management and care, you can continue to lead a healthy life. Here are some tips for managing your symptoms:
- Maintain a healthy diet and understand the foods that can impact your blood sugar levels
- Create an exercise plan with your doctor and stay active
- Try to avoid drinking alcohol or other high-sugar drinks
- Properly store your insulin and take medication as your doctor recommends
- Find ways to manage stress and relax your body
- Listen and follow any additional doctor recommendations
If you are finding it difficult to manage diabetes or are experiencing symptoms like memory loss, assisted living is a great way to create a support system and get the care you need.
Providing Support
Diabetes or memory loss is challenging to face alone, and sometimes seeking help and guidance is the first step to leading a happier and healthier life. Our compassionate team at Meadowcrest at Middletown is pleased to book a consultation to discuss the care we can provide.